Difference between revisions of "PcDuino9"
(→I2C RTC) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | == Introduction == |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:pcduino9 d.jpg|640px]] |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:pcduino9 b.jpg|640px]] |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:pcduino9 c.jpg|640px]] |
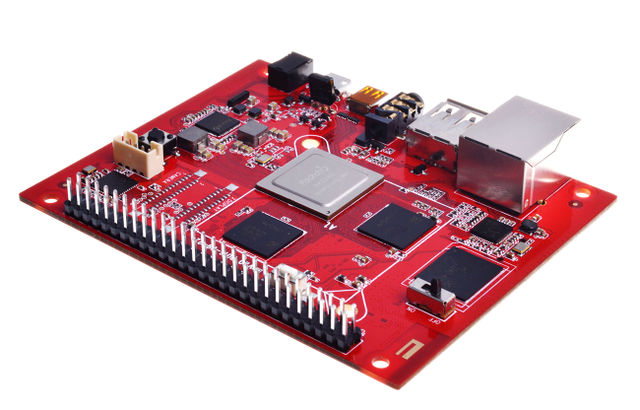
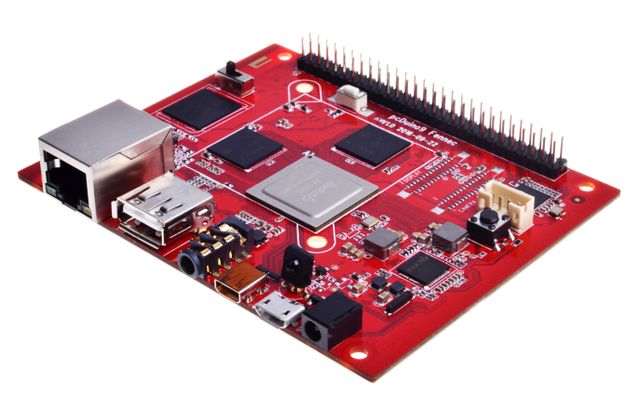
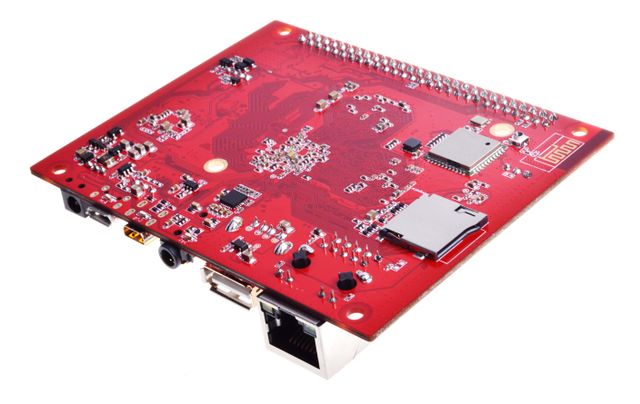
| − | + | PcDuino9 is a high-performance platform with powerful multi-threaded computing power, graphics processing and hardware decoding capabilities, and it supports Android and Ubuntu dual system, so it is also a powerful small computer, we hope that your creativity and inspiration will make it become more extraordinary. | |
| − | == | + | == Specifications == |
*CPU : Rockchip RK3288 ARM Corte-A17 Quad-Core up to 1.8GHz | *CPU : Rockchip RK3288 ARM Corte-A17 Quad-Core up to 1.8GHz | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
*Board Size : 96 x 76 mm | *Board Size : 96 x 76 mm | ||
| − | == | + | == Hardware specifications == |
| − | *CPU: Rockchip RK3288 ARM Corte-A17 Quad-Core up to 1.8GHz | + | *CPU : Rockchip RK3288 ARM Corte-A17 Quad-Core up to 1.8GHz |
| − | *GPU: ARM Mali-T760 MP4 Support OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0 /3.0, OpenVG1.1, OpenCL1.1, Directx11 | + | *GPU : ARM Mali-T760 MP4 Support OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0 /3.0, OpenVG1.1, OpenCL1.1, Directx11 |
| − | * | + | *Memory : 1GB-4GB Dual-channel 32-bit LPDDR3 |
| − | * | + | *Storage : 8GB-16GB eMMC (Opt.), Micro SD slot support SDXC |
| − | * | + | *Ethernet : 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet (RTL8211) |
| − | * | + | *USB : USB 2.0 Host x 2 (Opt.), USB OTG x 1 |
| − | * | + | *Video : HDMI2.0 support maximum 4K@60Hz display (Micro HDMI), LVDS/MIPI-DSI display interface |
| − | * | + | *Audio : 3.5mm audio In/Out |
| − | * | + | *Camera : MIPI-CSI camera interface |
| − | + | *WiFi/BT : AP6212 WiFi + BT module | |
| − | + | *IR: support infrared remote control function | |
| − | + | *GPIO Extension : Raspberry Pi compatible GPIO, support UART, SPI, I2C BMC extension GPIO (Opt.), support ADC, PWM, UART, I2C | |
| − | + | *Board Size : 96 x 76 mm | |
| − | + | *Power supply: DC -5V / 2.5A | |
| − | + | == GPIOs mapping == | |
| − | + | [[File:pcduino 9 d.png|640px]] | |
| − | === | + | === pcDuino9 === |
| − | + | [[File:pcduino 9 e.png|640px]] | |
| − | + | === BMC STM32F411 === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:pcduino9 f.png|640px]] | |
| − | + | == Quick Start == | |
| − | + | === 1.Write the system to eMMC by SD card === | |
| − | + | Download the image which named pcDuino9-SD-to-eMMC-xxx.img,use dd or Win32Disk,copy the image to SD card ,put the SD card on pcDuino9,and then pcDuino9 system on switch SD,that means switch the button “on” ,use ttl uart to watch system log,when kernel start,put the system on switch to “off”,then wait for all things done. | |
| + | System user name : linaro ,password:linaro | ||
| − | + | === 2.Write the system to eMMC on Linux === | |
| − | + | RK provides a command line tool of '''upgrade_tool''' under Linux, supporting for unified firmware '''update.img''' and partition image programming. | |
| − | + | There are two options for the open source tool: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*rkflashtool [https://github.com/Galland/rkflashtool_rk3066 https://github.com/Galland/rkflashtool_rk3066] | *rkflashtool [https://github.com/Galland/rkflashtool_rk3066 https://github.com/Galland/rkflashtool_rk3066] | ||
| Line 141: | Line 94: | ||
*rkflashkit [https://github.com/linuxerwang/rkflashkit https://github.com/linuxerwang/rkflashkit] | *rkflashkit [https://github.com/linuxerwang/rkflashkit https://github.com/linuxerwang/rkflashkit] | ||
| − | + | They only support the partition image programming, does not support a unified firmware. Rkflashtool is a command line tool, rkflashkit has a graphical interface and a command line support, which make it easier to use. The following only do an introduction of rkflashkit. There is no need to install the device driver for Linux, you can refer to the Windows chapter to connect the device. | |
'''upgrade_tool''' | '''upgrade_tool''' | ||
| − | + | Download Linux_Upgrade_Tool, and install to the system as the following method to be easy to call: | |
tar xf Linux_UpgradeTool_v1.2.tar.gz | tar xf Linux_UpgradeTool_v1.2.tar.gz | ||
| Line 152: | Line 105: | ||
sudo chown root:root /usr/local/bin/upgrade_tool | sudo chown root:root /usr/local/bin/upgrade_tool | ||
| − | + | Write unite firmware uxxxx.img: | |
sudo upgrade_tool uf update.img | sudo upgrade_tool uf update.img | ||
| − | + | Program partition image: | |
sudo upgrade_tool di -b /path/to/boot.img | sudo upgrade_tool di -b /path/to/boot.img | ||
| Line 164: | Line 117: | ||
sudo upgrade_tool di -m /path/to/misc.img | sudo upgrade_tool di -m /path/to/misc.img | ||
sudo upgrade_tool di resource /path/to/resource.img | sudo upgrade_tool di resource /path/to/resource.img | ||
| − | sudo upgrade_tool di -p paramater # | + | sudo upgrade_tool di -p paramater #Write parameter |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool ul bootloader.bin # | + | sudo upgrade_tool ul bootloader.bin #Write bootloader |
| + | |||
| − | + | If flash problems lead to an error during the upgrade, you can try low-level format or erase nand flash: | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool lf # | + | sudo upgrade_tool lf # low-level format |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool ef # | + | sudo upgrade_tool ef # erase nand flash |
'''rkflashkit''' | '''rkflashkit''' | ||
| − | + | Installation: | |
sudo apt-get install build-essential fakeroot | sudo apt-get install build-essential fakeroot | ||
| Line 183: | Line 137: | ||
sudo dpkg -i rkflashkit_0.1.2_all.deb | sudo dpkg -i rkflashkit_0.1.2_all.deb | ||
| − | + | Graphic interface: | |
sudo rkflashkit | sudo rkflashkit | ||
| Line 189: | Line 143: | ||
[[File:pcduino 9 l.png|640px]] | [[File:pcduino 9 l.png|640px]] | ||
| − | + | Command Line: | |
$ rkflashkit --help | $ rkflashkit --help | ||
| Line 202: | Line 156: | ||
sudo rkflashkit flash @boot boot.img @kernel.img kernel.img reboot | sudo rkflashkit flash @boot boot.img @kernel.img kernel.img reboot | ||
| − | === 3. | + | === 3.SD card boot system === |
| − | * | + | *Download the xxxx.img system image |
| − | * | + | *Prepare a memory card (C10 of more than 4GB) |
| − | * | + | *Use the dd command to copy the system to SD |
| − | * | + | *Insert the card into the pcDuino9, press the MASKROM button starting from the TF card to boot. |
| − | === 4. | + | === 4.pcDuino9 hardware operation === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Hardware operation is based on '''NightWiring''', which is a hardware interface controlled by a cross-platform C ++ library, including UART, I2C, SPI and GPIO.Most of the code can be downloaded from wiringpi. GPIO is based on the function of the sysfs, it will be slightly slower, but very flexible. | ||
*git clone [https://github.com/nightseas/nightWiring.git https://github.com/nightseas/nightWiring.git] | *git clone [https://github.com/nightseas/nightWiring.git https://github.com/nightseas/nightWiring.git] | ||
| Line 223: | Line 176: | ||
sudo make install | sudo make install | ||
| − | ==== GPIO | + | ==== GPIO LED control ==== |
#include "nightWiring.h" | #include "nightWiring.h" | ||
| Line 265: | Line 218: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | ==== GPIO | + | ==== GPIO key input ==== |
#include "nightWiring.h" | #include "nightWiring.h" | ||
| Line 392: | Line 345: | ||
return 0; | return 0; | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Produce pcDuino9 system image == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Preparations === | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Download pcDuino9 kernel [http://pan.baidu.com/s/1slB59XN kernel.tar.gz] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Download pcDuino9 uboot [http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hsjxHp6 u-boot.tar.gz] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Download root file system of pcDuino9 [https://pan.baidu.com/s/1eSE1tfW#list/path=%2F rockchip] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Create a directory called rk-linux in the linux host, and then download the uboot, kernel and root file system into this file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === The necessary environment for the installation === | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note: Please use the 5.x version for the GCC version''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo apt-get install git-core gitk git-gui gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf u-boot-tools device-tree-compiler gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu | ||
| + | sudo apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf libssl-dev gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Compile the kernel === | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd rk-linux/kernel/ | ||
| + | make clean | ||
| + | make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- rockchip_linux_defconfig | ||
| + | make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- -j4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Compile uboot === | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd /rk-linux/u-boot/ | ||
| + | make distclean | ||
| + | CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- make fennec-rk3288_defconfig all | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Produce boot.img === | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Produce uboot-spl.img | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd rk-linux/ | ||
| + | u-boot/tools/mkimage -n rk3288 -T rksd -d u-boot/spl/u-boot-spl-dtb.bin uboot-spl.img | ||
| + | cat u-boot/u-boot-dtb.bin >> uboot-spl.img | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Produce extlinux.conf === | ||
| + | |||
| + | vim extlinux.comf | ||
| + | |||
| + | label kernel-4.4 | ||
| + | kernel /zImage | ||
| + | fdt /rk3288-fennec.dtb | ||
| + | append earlyprintk console=ttyS2,115200n8 rw root=/dev/mmcblk1p7 rootfstype=ext4 init=/sbin/init | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Produce boot.img | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd rk-linux/ | ||
| + | sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=boot.img bs=1M count=128 | ||
| + | sudo mkfs.fat boot.img | ||
| + | mkdir boot | ||
| + | sudo mount boot.img boot | ||
| + | sudo cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/zImage boot | ||
| + | sudo cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/dts/rk3288-fennec.dtb boot | ||
| + | sudo mkdir boot/extlinux | ||
| + | sudo cp extlinux.conf boot/extlinux | ||
| + | sudo umount boot | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Download the root file system === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Download the root file system and rename it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | mv linaro-rootfs.img rootfs.img | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Create a card update system === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Download [http://pan.baidu.com/s/1bPrkUq initrd.img] | ||
| + | | ||
| + | *Format the SD card | ||
| + | |||
| + | chen@chen-HP-ProDesk-680-G1-TWR:~/work/linaro-alip/ramdisk/update$ sudo gdisk /dev/sdb | ||
| + | GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.8 | ||
| + | Partition table scan: | ||
| + | MBR: protective | ||
| + | BSD: not present | ||
| + | APM: not present | ||
| + | GPT: present | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Found valid GPT with protective MBR; using GPT. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Command (? for help): o | ||
| + | This option deletes all partitions and creates a new protective MBR. | ||
| + | Proceed? (Y/N): y | ||
| + | |||
| + | Command (? for help): n | ||
| + | Partition number (1-128, default 1): 1 | ||
| + | First sector (34-126613470, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: 8192 | ||
| + | Last sector (8192-126613470, default = 126613470) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: | ||
| + | Current type is 'Linux filesystem' | ||
| + | Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): | ||
| + | Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Command (? for help): w | ||
| + | Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING | ||
| + | PARTITIONS!! | ||
| + | Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y | ||
| + | OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdc. | ||
| + | Warning: The kernel is still using the old partition table. | ||
| + | The new table will be used at the next reboot. | ||
| + | The operation has completed successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | sudo umount /dev/sdb1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo mkfs.fat /dev/sdb1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | sudo dd if=uboot-spl.img of=/dev/sdb seek=64 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Copy zimage, dts and ramdisk to /dev/sdb1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd rk-linux/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/zImage /media/chen/9F35-9565/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/dts/rk3288-fennec.dtb /media/ls/9F35-9565/rk3288-fennec.dtb | ||
| + | |||
| + | cp ../rk-initrd-build/initrd.img /media/ls/9F35-9565/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Add extlinux/extlinux.conf in the dev/sdb1/directory | ||
| + | |||
| + | label kernel-4.4 | ||
| + | kernel /zImage | ||
| + | fdt /rk3288-fennec.dtb | ||
| + | initrd /initrd.img | ||
| + | append earlyprintk console=ttyS2,115200n8 rw root=/dev/ram0 rootfstype=ext4 init=/sbin/init ramdisk_size=49152 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Copy u-boot-dtb.img, uboot-spl.img, boot.img, rootfs.img and update.sh to /dev/sdb1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | mkdir /media/chen/9F35-9565/update | ||
| + | cp uboot-spl.img /media/chen/9F35-9565/update | ||
| + | cp boot.img /media/chen/9F35-9565/update | ||
| + | cp rootfs.img /media/chen/9F35-9565/update | ||
| + | cp update.sh /media/chen/9F35-9565/update | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Update the pcDuino9 system via SD card == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Insert the SD card into the pcDuino9, and set the switch to the startup mode. When the kernel is up, set the switch to start the eMMC. When the system is up, you can see that the system image is being programmed into eMMC. | ||
Latest revision as of 06:54, 19 January 2017
Contents
Introduction
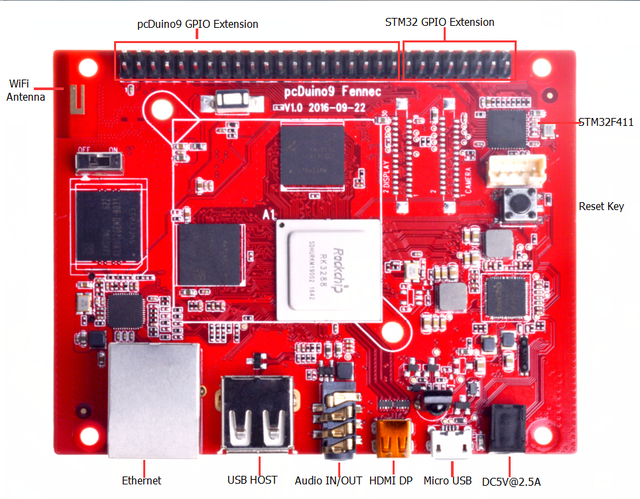
PcDuino9 is a high-performance platform with powerful multi-threaded computing power, graphics processing and hardware decoding capabilities, and it supports Android and Ubuntu dual system, so it is also a powerful small computer, we hope that your creativity and inspiration will make it become more extraordinary.
Specifications
- CPU : Rockchip RK3288 ARM Corte-A17 Quad-Core up to 1.8GHz
- GPU : ARM Mali-T760 MP4 Support OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0 /3.0, OpenVG1.1, OpenCL1.1, Directx11
- Memory : 1GB-4GB Dual-channel 32-bit LPDDR3
- Storage : 8GB-16GB eMMC (Opt.), Micro SD slot support SDXC
- Ethernet : 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet (RTL8211)
- USB : USB 2.0 Host x 2 (Opt.), USB OTG x 1
- Video : HDMI2.0 support maximum 4K@60Hz display (Micro HDMI), LVDS/MIPI-DSI display interface
- Audio : 3.5mm audio In/Out
- Camera : MIPI-CSI camera interface
- WiFi/BT : AP6212 WiFi + BT module
- GPIO Extension : Raspberry Pi compatible GPIO, support UART, SPI, I2C BMC extension GPIO (Opt.), support ADC, PWM, UART, I2C
- Board Size : 96 x 76 mm
Hardware specifications
- CPU : Rockchip RK3288 ARM Corte-A17 Quad-Core up to 1.8GHz
- GPU : ARM Mali-T760 MP4 Support OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0 /3.0, OpenVG1.1, OpenCL1.1, Directx11
- Memory : 1GB-4GB Dual-channel 32-bit LPDDR3
- Storage : 8GB-16GB eMMC (Opt.), Micro SD slot support SDXC
- Ethernet : 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet (RTL8211)
- USB : USB 2.0 Host x 2 (Opt.), USB OTG x 1
- Video : HDMI2.0 support maximum 4K@60Hz display (Micro HDMI), LVDS/MIPI-DSI display interface
- Audio : 3.5mm audio In/Out
- Camera : MIPI-CSI camera interface
- WiFi/BT : AP6212 WiFi + BT module
- IR: support infrared remote control function
- GPIO Extension : Raspberry Pi compatible GPIO, support UART, SPI, I2C BMC extension GPIO (Opt.), support ADC, PWM, UART, I2C
- Board Size : 96 x 76 mm
- Power supply: DC -5V / 2.5A
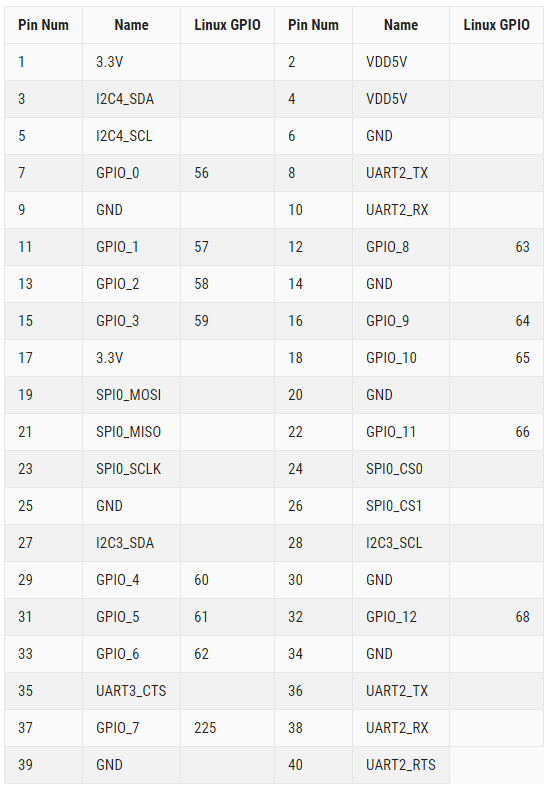
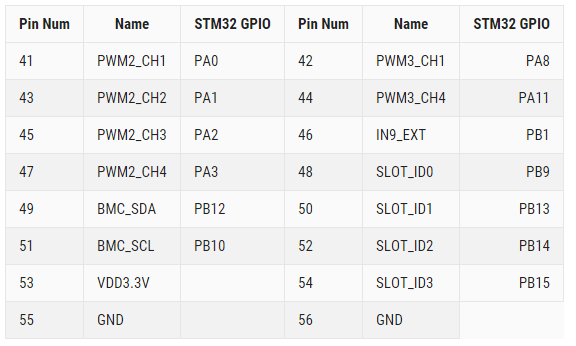
GPIOs mapping
pcDuino9
BMC STM32F411
Quick Start
1.Write the system to eMMC by SD card
Download the image which named pcDuino9-SD-to-eMMC-xxx.img,use dd or Win32Disk,copy the image to SD card ,put the SD card on pcDuino9,and then pcDuino9 system on switch SD,that means switch the button “on” ,use ttl uart to watch system log,when kernel start,put the system on switch to “off”,then wait for all things done. System user name : linaro ,password:linaro
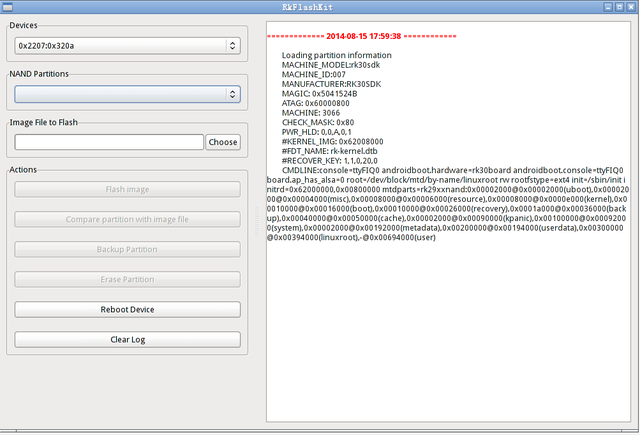
2.Write the system to eMMC on Linux
RK provides a command line tool of upgrade_tool under Linux, supporting for unified firmware update.img and partition image programming.
There are two options for the open source tool:
- rkflashtool https://github.com/Galland/rkflashtool_rk3066
- rkflashkit https://github.com/linuxerwang/rkflashkit
They only support the partition image programming, does not support a unified firmware. Rkflashtool is a command line tool, rkflashkit has a graphical interface and a command line support, which make it easier to use. The following only do an introduction of rkflashkit. There is no need to install the device driver for Linux, you can refer to the Windows chapter to connect the device.
upgrade_tool
Download Linux_Upgrade_Tool, and install to the system as the following method to be easy to call:
tar xf Linux_UpgradeTool_v1.2.tar.gz cd Linux_UpgradeTool_v1.2 sudo mv upgrade_tool /usr/local/bin sudo chown root:root /usr/local/bin/upgrade_tool
Write unite firmware uxxxx.img:
sudo upgrade_tool uf update.img
Program partition image:
sudo upgrade_tool di -b /path/to/boot.img sudo upgrade_tool di -k /path/to/kernel.img sudo upgrade_tool di -s /path/to/system.img sudo upgrade_tool di -r /path/to/recovery.img sudo upgrade_tool di -m /path/to/misc.img sudo upgrade_tool di resource /path/to/resource.img sudo upgrade_tool di -p paramater #Write parameter sudo upgrade_tool ul bootloader.bin #Write bootloader
If flash problems lead to an error during the upgrade, you can try low-level format or erase nand flash:
sudo upgrade_tool lf # low-level format sudo upgrade_tool ef # erase nand flash
rkflashkit
Installation:
sudo apt-get install build-essential fakeroot git clone https://github.com/linuxerwang/rkflashkit cd rkflashkit ./waf debian sudo apt-get install python-gtk2 sudo dpkg -i rkflashkit_0.1.2_all.deb
Graphic interface:
sudo rkflashkit
Command Line:
$ rkflashkit --help Usage: <cmd> [args] [<cmd> [args]...] part List partition flash @<PARTITION> <IMAGE FILE> Flash partition with image file cmp @<PARTITION> <IMAGE FILE> Compare partition with image file backup @<PARTITION> <IMAGE FILE> Backup partition to image file erase @<PARTITION> Erase partition reboot Reboot device For example, flash device with boot.img and kernel.img, then reboot: sudo rkflashkit flash @boot boot.img @kernel.img kernel.img reboot
3.SD card boot system
- Download the xxxx.img system image
- Prepare a memory card (C10 of more than 4GB)
- Use the dd command to copy the system to SD
- Insert the card into the pcDuino9, press the MASKROM button starting from the TF card to boot.
4.pcDuino9 hardware operation
Hardware operation is based on NightWiring, which is a hardware interface controlled by a cross-platform C ++ library, including UART, I2C, SPI and GPIO.Most of the code can be downloaded from wiringpi. GPIO is based on the function of the sysfs, it will be slightly slower, but very flexible.
cd nightWiring/ make -j4 sudo make install
GPIO LED control
#include "nightWiring.h"
#include "nightWiringGPIO.h"
#include "stdio.h"
static int fennecGpioMap[] = {
/* GPIO2_A0 */
56,
/* GPIO2_A1, GPIO2_A2, GPIO2_A3, GPIO2_A4 */
57, 58, 59, 60,
/* GPIO2_A5, GPIO2_A6, GPIO7_B1, GPIO2_A7 */
61, 62, 225, 63,
/* GPIO2_B0, GPIO2_B1, GPIO2_B2, GPIO2_B4 */
64, 65, 66, 68,
/* GPIO2_B5, GPIO7_B0, GPIO7_A7, GPIO7_B2 */
69, 224, 223, 226
};
int ledMap[] = {2, 10, 3, 11};
int main(void)
{
int i, j;
nightWiringSetup();
nightWiringGpioSetup(fennecGpioMap, 17);
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
pinMode(ledMap[i], OUTPUT);
while(1)
{
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<4; j++)
digitalWrite(ledMap[j], HIGH);
digitalWrite(ledMap[i], LOW);
delay(500);
}
}
return 0;
}
GPIO key input
#include "nightWiring.h"
#include "nightWiringGPIO.h"
#include "stdio.h"
static int fennecGpioMap[] = {
/* GPIO2_A0 */
56,
/* GPIO2_A1, GPIO2_A2, GPIO2_A3, GPIO2_A4 */
57, 58, 59, 60,
/* GPIO2_A5, GPIO2_A6, GPIO7_B1, GPIO2_A7 */
61, 62, 225, 63,
/* GPIO2_B0, GPIO2_B1, GPIO2_B2, GPIO2_B4 */
64, 65, 66, 68,
/* GPIO2_B5, GPIO7_B0, GPIO7_A7, GPIO7_B2 */
69, 224, 223, 226
};
int keyMap[] = {6, 13, 4, 12, 5};
char keyName[5][7] = {"UP\0", "CENTER\0", "DOWN\0", "LEFT\0", "RIGHT\0"};
int readKey(int num)
{
int key = digitalRead(keyMap[num]);
if(key == LOW)
{
// Delay for a while and re-detect the key status
// Filtering glitches on the signal
delay(10);
if(key == LOW)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
nightWiringSetup();
nightWiringGpioSetup(fennecGpioMap, 17);
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
pinMode(keyMap[i], INPUT);
while(1)
{
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
{
if(readKey(i))
{
printf("Key %s is pressed!\n", keyName[i]);
delay(500);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
I2C RTC
#include "nightWiring.h"
#include "nightWiringI2C.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#define DS1307_ADDR 0x68
int i2cFd;
int quitFlag = 0;
unsigned char DEC2BCD(unsigned char val)
{
return ( (val/10*16) + (val%10) );
}
unsigned char BCD2DEC(unsigned char val)
{
return ( (val/16*10) + (val%16) );
}
void rtcSetTime(unsigned char year, unsigned char month, unsigned char date, unsigned char dayofWeek, unsigned char hour, unsigned char min ,unsigned char sec)
{
unsigned char reg = 0x00;
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x00, DEC2BCD(sec));
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x01, DEC2BCD(min));
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x02, DEC2BCD(hour));
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x03, DEC2BCD(dayofWeek));
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x04, DEC2BCD(date));
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x05, DEC2BCD(month));
i2cWriteReg8(i2cFd, 0x06, DEC2BCD(year));
}
void rtcGetTime()
{
unsigned char year, month, date, dayofWeek, hour, min ,sec;
unsigned char reg = 0x00;
sec = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x00) & 0x7f);
min = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x01));
hour = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x02) & 0x3f);
dayofWeek = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x03));
date = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x04));
month = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x05));
year = BCD2DEC(i2cReadReg8(i2cFd, 0x06));
printf("Time: %02d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.\n", year, month, date, hour, min ,sec);
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
if((i2cFd=i2cSetup("/dev/i2c-4", DS1307_ADDR)) < 0)
{
printf("Error: I2C acess failed! i2cSetup() return %d\n",i2cFd);
return 0;
}
printf("I2C interface init complete.\n");
printf("Writing time 2016-10-01 Sat 21:10:00 to RTC...\n");
rtcSetTime(16,10,1,6,21,10,0);
while(1)
{
rtcGetTime();
delay(1000);
}
return 0;
}
Produce pcDuino9 system image
Preparations
- Download pcDuino9 kernel kernel.tar.gz
- Download pcDuino9 uboot u-boot.tar.gz
- Download root file system of pcDuino9 rockchip
Create a directory called rk-linux in the linux host, and then download the uboot, kernel and root file system into this file.
The necessary environment for the installation
Note: Please use the 5.x version for the GCC version
sudo apt-get install git-core gitk git-gui gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf u-boot-tools device-tree-compiler gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu sudo apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf libssl-dev gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu
Compile the kernel
cd rk-linux/kernel/ make clean make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- rockchip_linux_defconfig make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- -j4
Compile uboot
cd /rk-linux/u-boot/ make distclean CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- make fennec-rk3288_defconfig all
Produce boot.img
- Produce uboot-spl.img
cd rk-linux/ u-boot/tools/mkimage -n rk3288 -T rksd -d u-boot/spl/u-boot-spl-dtb.bin uboot-spl.img cat u-boot/u-boot-dtb.bin >> uboot-spl.img
Produce extlinux.conf
vim extlinux.comf
label kernel-4.4
kernel /zImage
fdt /rk3288-fennec.dtb
append earlyprintk console=ttyS2,115200n8 rw root=/dev/mmcblk1p7 rootfstype=ext4 init=/sbin/init
- Produce boot.img
cd rk-linux/ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=boot.img bs=1M count=128 sudo mkfs.fat boot.img mkdir boot sudo mount boot.img boot sudo cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/zImage boot sudo cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/dts/rk3288-fennec.dtb boot sudo mkdir boot/extlinux sudo cp extlinux.conf boot/extlinux sudo umount boot
Download the root file system
Download the root file system and rename it.
mv linaro-rootfs.img rootfs.img
Create a card update system
Download initrd.img
- Format the SD card
chen@chen-HP-ProDesk-680-G1-TWR:~/work/linaro-alip/ramdisk/update$ sudo gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.8
Partition table scan:
MBR: protective
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: present
Found valid GPT with protective MBR; using GPT.
Command (? for help): o
This option deletes all partitions and creates a new protective MBR.
Proceed? (Y/N): y
Command (? for help): n
Partition number (1-128, default 1): 1
First sector (34-126613470, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: 8192
Last sector (8192-126613470, default = 126613470) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300):
Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem'
Command (? for help): w
Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING
PARTITIONS!!
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y
OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdc.
Warning: The kernel is still using the old partition table.
The new table will be used at the next reboot.
The operation has completed successfully.
sudo umount /dev/sdb1 sudo mkfs.fat /dev/sdb1
sudo dd if=uboot-spl.img of=/dev/sdb seek=64
- Copy zimage, dts and ramdisk to /dev/sdb1
cd rk-linux/ cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/zImage /media/chen/9F35-9565/ cp kernel/arch/arm/boot/dts/rk3288-fennec.dtb /media/ls/9F35-9565/rk3288-fennec.dtb cp ../rk-initrd-build/initrd.img /media/ls/9F35-9565/
- Add extlinux/extlinux.conf in the dev/sdb1/directory
label kernel-4.4
kernel /zImage
fdt /rk3288-fennec.dtb
initrd /initrd.img
append earlyprintk console=ttyS2,115200n8 rw root=/dev/ram0 rootfstype=ext4 init=/sbin/init ramdisk_size=49152
- Copy u-boot-dtb.img, uboot-spl.img, boot.img, rootfs.img and update.sh to /dev/sdb1
mkdir /media/chen/9F35-9565/update cp uboot-spl.img /media/chen/9F35-9565/update cp boot.img /media/chen/9F35-9565/update cp rootfs.img /media/chen/9F35-9565/update cp update.sh /media/chen/9F35-9565/update
Update the pcDuino9 system via SD card
Insert the SD card into the pcDuino9, and set the switch to the startup mode. When the kernel is up, set the switch to start the eMMC. When the system is up, you can see that the system image is being programmed into eMMC.