Difference between revisions of "ESP8266 Serial WIFI Module"
(→Description) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
*x is the commands | *x is the commands | ||
| − | { | + | {|class="wikitable" |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !'''set''' |
| − | ! | + | !!'''inquiriy''' |
| − | ! | + | !!'''test''' |
| − | ! | + | !!'''execute''' |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | AT+<x>=<…>||AT+<x>?||AT+<x>?||AT+<x> | ! scope="row" | AT+<x>=<…>||AT+<x>?||AT+<x>?||AT+<x> | ||
Revision as of 05:27, 3 November 2015
Description
ESP8266 offers a complete and self-contained Wi-Fi networking solution, allowing it to either host the application or to offload all Wi-Fi networking functions from another application processor.
When ESP8266 hosts the application, and when it is the only application processor in the device, it is able to boot up directly from an external flash. It has integrated cache to improve the performance of the system in such applications, and to minimize the memory requirements.
Alternately, serving as a Wi-Fi adapter, wireless internet access can be added to any microcontroller-based design with simple connectivity through UART interface or the CPU AHB bridge interface.
ESP8266 on-board processing and storage capabilities allow it to be integrated with the sensors and other application specific devices through its GPIOs with minimal development up-front and minimal loading during runtime. With its high degree of on-chip integration, which includes the antenna switch balun, power management converters, it requires minimal external circuitry, and the entire solution, including front-end module, is designed to occupy minimal PCB area.
Sophisticated system-level features include fast sleep/wake context switching for energy-efficient VoIP, adaptive radio biasing for low-power operation, advance signal processing, and spur cancellation and radio co-existence features for common cellular, Bluetooth, DDR, LVDS, LCD interference mitigation.
Features:
- 802.11 b/g/n protocol
- Wi-Fi Direct (P2P), soft-AP
- Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
- Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
- Integrated PLL, regulators, and power management units
- +19.5dBm output power in 802.11b mode
- Integrated temperature sensor
- Supports antenna diversity
- Power down leakage current of < 10uA
- Integrated low power 32-bit CPU could be used as application processor
- SDIO 2.0, SPI, UART
- STBC, 1×1 MIMO, 2×1 MIMO
- A-MPDU & A-MSDU aggregation & 0.4us guard interval
- Wake up and transmit packets in < 2ms
- Standby power consumption of < 1.0mW (DTIM3)
Electronic Characteristic
1. Current Consumption:
The following current consumption is based on 3.3V supply, and 25℃ ambient, using internal regulators. Measurements are done at antenna port without SAW filter. All the transmitter’s measurements are based on 90% duty cycle, continuous transmit mode.
2.RF Performance
The following are measured under room temperature conditions with 3.3V and 1.1V power supplies.
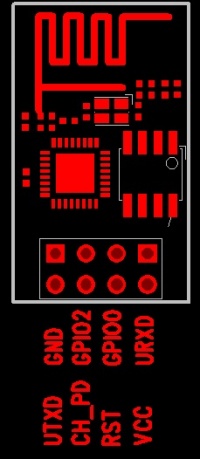
Hardware:
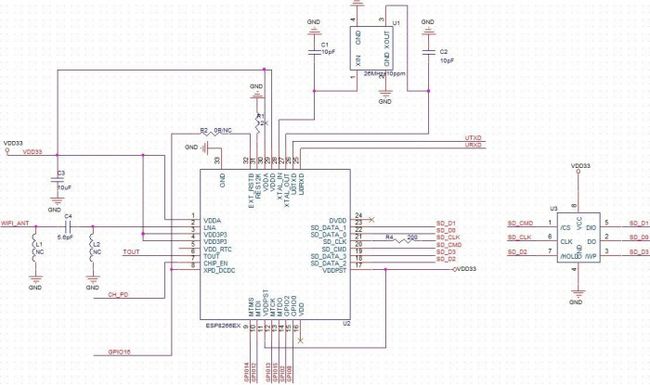
Schematic:
Application fields:
- Smart power plugs
- Home automation
- Mesh network
- Industrial wireless control
- Baby monitors
- IP Cameras
- Sensor networks
- Wearable electronics
- Wi-Fi location-aware devices
- Security ID tags
- Wi-Fi position system beacons
AT Commands:
Format
- Baud rate at 57600, was actually 9600 as reported by Alan
- x is the commands
Download
Example of Using it
- http://www.instructables.com/id/Using-the-ESP8266-module/
- The ESP8266 Becomes a Terrible Browser - http://hackaday.io/project/3072/instructions
- New Working GCC for ESP8266 - http://www.esp8266.com/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=224
- http://blog.iteadstudio.com/esp8266-use-android-phone-to-control-itead-rboard/
- SDK for ESP8266 - http://hackaday.com/2014/10/25/an-sdk-for-the-esp8266-wifi-chip/
- An ESP8266 Based Smartmeter - http://hackaday.com/2014/10/25/an-sdk-for-the-esp8266-wifi-chip/
Demos for ESP8266
How to buy
Here to buy ESP8266 Serial WIFI Module on store
| set | !inquiriy | !test | !execute |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT+<x>=<…> | AT+<x>? | AT+<x>? | AT+<x> |