Infrared Distance Sensor
Introduction
The Sharp distance sensors are a popular choice for many projects that require accurate distance measurements. This IR sensor is more economical than sonar rangefinders, yet it provides much better performance than other IR alternatives. Interfacing to most microcontrollers is straightforward: the single analog output can be connected to an analog-to-digital converter for taking distance measurements, or the output can be connected to a comparator for threshold detection. The detection range of this version is approximately 10 cm to 80 cm (4" to 32"); a plot of distance versus output voltage is shown below.
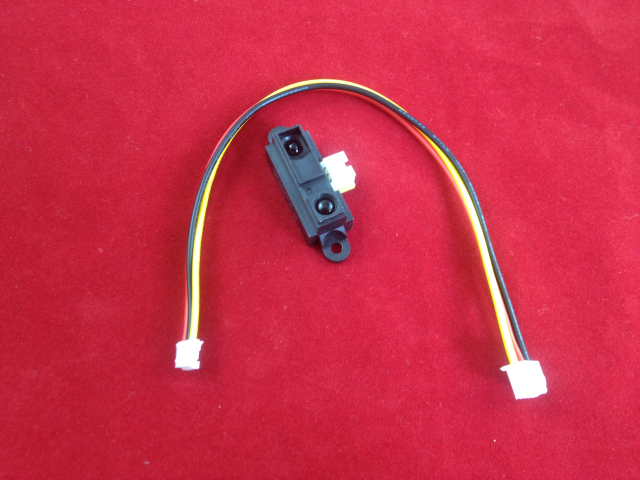
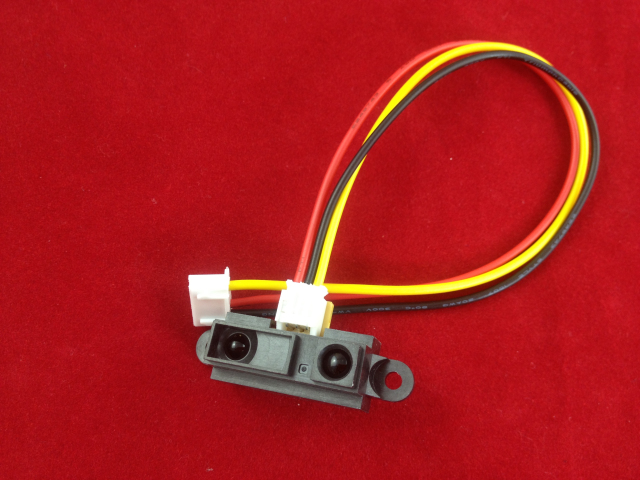
The GP2Y0A21 uses a 3-pin JST connector that works with our 3-pin JST cables for Sharp distance sensors (not included) as shown in the upper picture on the right. It is also simple to solder three wires to the sensor where the connector pins are mounted (see the lower picture to the right). When looking at the back, the three connections from left to right are power, ground, and the output signal.
Features
- operating voltage: 4.5 V to 5.5 V
- average current consumption: 30 mA (typical)
- distance measuring range: 10 cm to 80 cm (4" to 32")
- output type: analog voltage
- output voltage differential over distance range: 1.9 V (typical)
- response time: 38 ± 10 ms
- package size: 29.5×13.0×13.5 mm (1.16×0.5×0.53")
- weight: 3.5 g (0.12 oz)
Application Ideas
test <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> int sensorPin = 0; void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //Start the serial connection with the computer
//to view the result open the serial monitor
}
void loop() // run over and over again {
//getting the voltage reading from the temperature sensor
int reading = analogRead(sensorPin);
// converting that reading to voltage, for 3.3v arduino use 3.3
float voltage = reading * 5.0;
voltage /= 1023.0;
// print out the voltage
Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println(" volts");
delay(1000); //waiting a second
} </syntaxhighlight>