3G + GPS Shield for Arduino
Contents
Introduction
The new 3G shield for Arduino enables the connectivity to high speed WCDMA and HSPA cellular networks in order to make possible the creation of the next level of worldwide interactivity projects inside the new "Internet of Things" era.
The module counts also with an internal GPS what enables the location of the device outdoors and indoors combining standard NMEA frames with mobile cell ID triangulation using both assisted-mobile (A-GPS) and mobile-based (S-GPS) modes.
Other interesting accessories which can be connected to the module are a video camera which enables the record of video in high resolution (640x480), an audio kit including microphone, speaker, hands free and headphones sets and a SD socket to save directly all the data coming from the 3G network or recorded from the video camera. You can even reproduce audio files stored in the SD card (like a mp3 player!).
You can also use it as a standard 3G modem at full speed (~7.2Mbps download, ~5.5Mbps upload) just connecting it through its specific mini-USB socket to your laptop (Linux, Windows, MacOS).
The new communicating module is specially oriented to work with Internet servers implementing internally several application layer protocols which make easier to send the information to the cloud. We can make HTTP and HTTPS (secure mode) navigation, downloading and uploading content to a web server. In the same way FTP and FTPS (secure mode) protocols are also available which is really useful when your application requires handling files. You can even send and receive mails directly from Arduino using the SMTP and POP3 clients implemented internally.
With the SD Card socket so you can handle a complete FAT16 file systems and store up to 32GB of information. This specially useful as the 3G module can work at full speed (~7.2Mbps download, ~5.5Mbps upload) when working with the SD files directly without need of Arduino for data or files management.
The GPS module also makes possible perform geolocation services even in indoors as it can work in A-GPS and S-GPS modes, so the location given by the GPS through NMEA sentences is completed with the cell information provided by both the 3G module and external Internet Geoposition Servers which helps you to get the most accurate location in each case.
Features
- WCDMA and HSPA 3G networks compatibility
- Internal GPS for Assisted A-GPS and Supported S-GPS modes
- Video Camera (640x480) for video and photo recordings available
- Audio Kit including microphone, speaker, hands free and headphones available
- SD file system up to 32GB
- Works as a standard 3G modem in Linux/Windows/MacOS (~7.2Mbps download, ~5.5Mbps upload)
- Talk directly to web servers by HTTP/HTTPS (secure)
- Upload and download files directly by FTP/FTPS (secure)
- Send and receive mails by POP3/SMTP
- Play compressed audio files
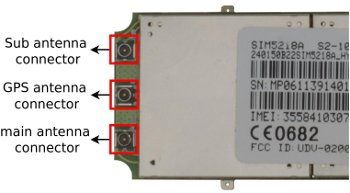
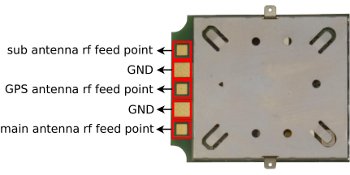
Antennas
Connections
SIM5218 has 3 UFL connectors. Two for diversity of 3G mobile carriers and one for GPS antenna. The impedance of the RF interface is 50Ω. It is recommended use just the "main" antenna socket for the mobile connection unless you experience coverage or performance problems. In this case two antennas allowing diversity may be placed.
Also, the module allows to solder the antenna to the pad, or attach it via contact springs.
Bandwidth
3G module connected with Arduino allows downlinks rates over 115200 bauds (~11.5KBps), the maximum UART's speed and uplinks rates over 30000 bauds (~3KBps).
Using the module as 3G USB modem we got speeds of 2Mbps (~222KBps) for downlink and 0.7Mbps (~77KBps) for uplink and.
The connection speed may vary depending on the state of the network, the quality of the signal and the carrier.
Using 3G module with AT commands
Important issues:
- Use capital letters for AT commands.
- Send CR (Carriage return) and LF (Line feed) after the AT command.
- Place the serial communication jumpers in the right position.
- Use an external power supply and place the power jumpers in the right position. If the shield is powered from the Arduino, the power jumper must be in Arduino 5V position. If the shield is powered from the Vin input (in the shield), the power jumper must be in Vext position.
The first thing we are going to do with the module is to connect the module to a PC directly (using an Arduino as gateway) and check the basic AT commands. In this case, serial communication jumpers have to be set on USB gateway position.
Remember take out the ATmega microcontroller from the Arduino gateway.
Basic configuration:
Connect the shield to the Arduino gateway.
Then connect the SIM card and the USB cable.
Finally plug the USB cable to the computer and open a serial port terminal to communicate via the usb port (e.g: hyperterminal (win), cutecom / gtkterm (linux)).
If you use the Arduino IDE serial monitor for sending AT commands – Be sure that you are sending CR (Carriage return) and LF (Line Feed).
Set the baudrate to 115200 bps and open the serial port, then press the ON button for two seconds. Then if you type AT you'll get OK, this means that the communication with the module is working fine. Now, with the module working you can check some AT commands to control the module, the basic commands are:
Important type commands in capital letters and with CR (carriage return) and LF (line feed)!!!
| Command | Respone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AT | OK | If you get OK, the communication with the module is working |
| AT+CPIN="****" | OK | If the SIM card is locked with PIN (**** is the pin number) |
| AT+COPS? | Operator information |