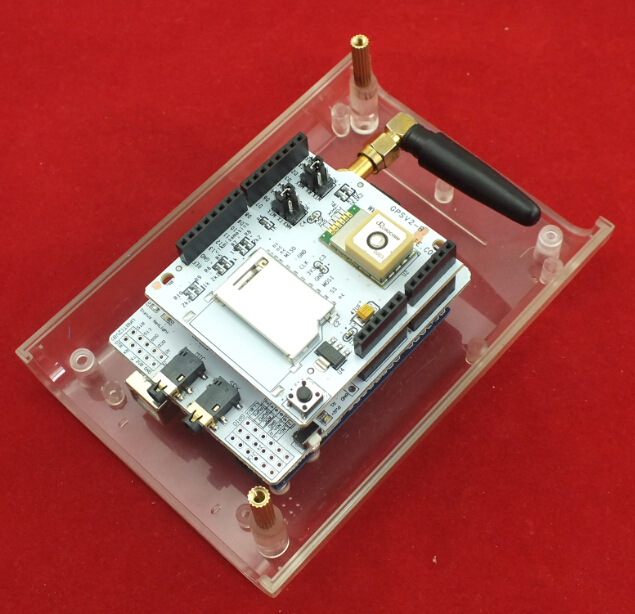
The Global Car Tracking Kit
Contents
Introduction
Every year about 700,000 vehicles get stolen in US. In fact, a car is stolen every 45 seconds.
In this instructable, I have explained the process of building one's very own Global Car Tracking System. The steps for building this device is very simple and explained in a lucid manner. The skills required for you to build this is minimum (Basic knowledge about electronics and the Arduino IDE).
Part List
1X Arduino Uno
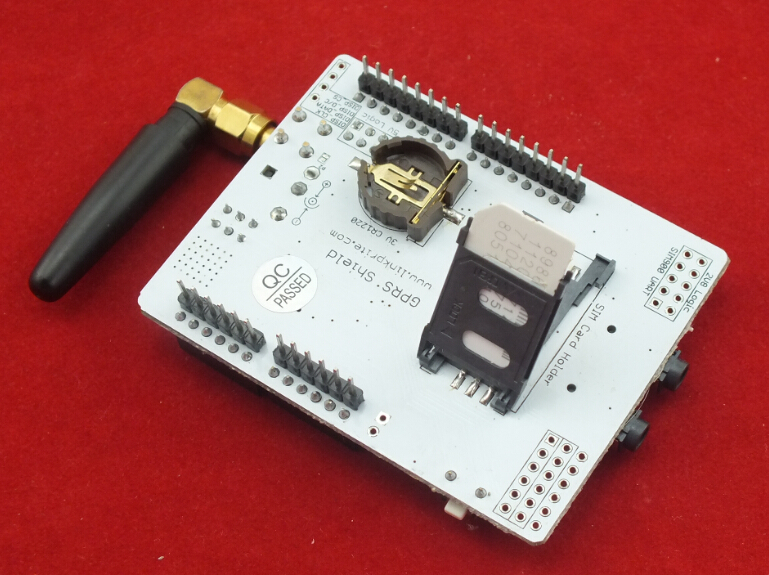
1X SIM900 GPRS/GSM Shield [SHD_SIM900][101101029]
1X GPS Shield With SD Card Slot for Arduino V2.0 B[SHD_GPSV2_B][101102006]
1X Adapter Plug for powering the Arduino
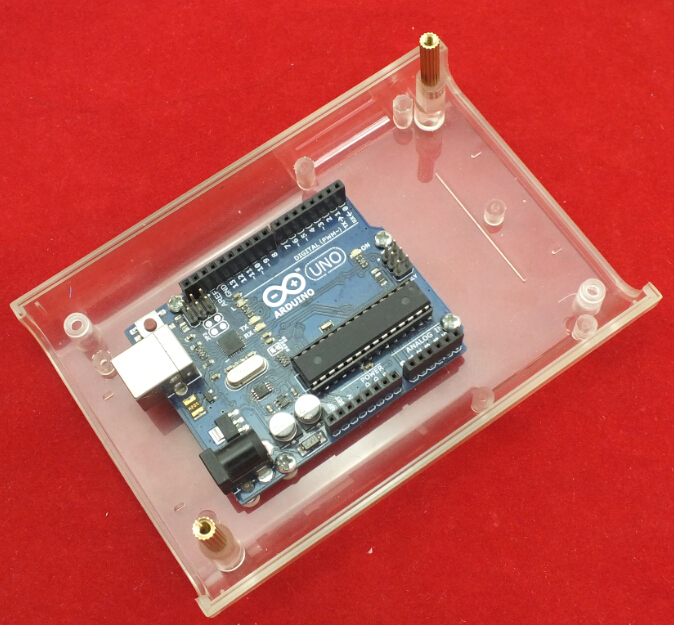
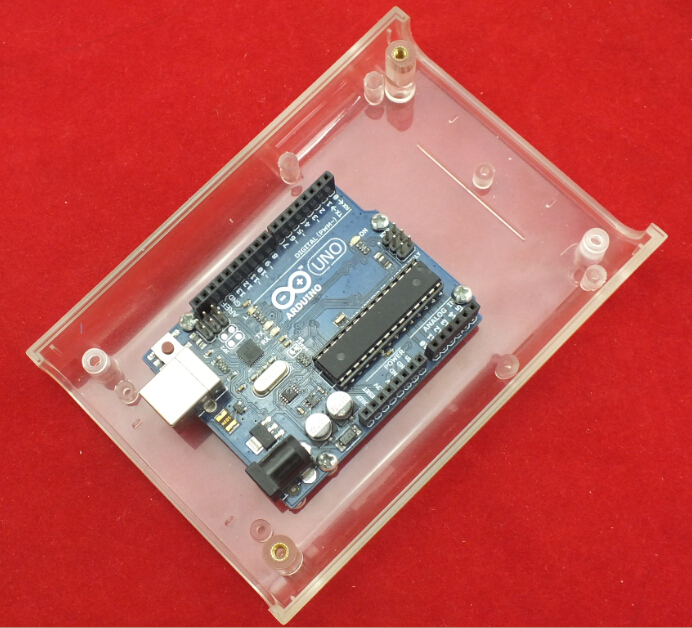
1X LinkSprite Clear Enclosure for pcDuino/Arduino[COM_CASE_PCDUINO_CLEAR] [114201005]
1X LinkSprite Extension Plate for Clear Enclosure for pcDuino/Arduino [COM_CASE_ARDU_CLEAR_PLATE][114201003]
Tools
1. Soldering Iron
2. Solder
3. Soldering Wax
4. Screw driver
HardWare set up
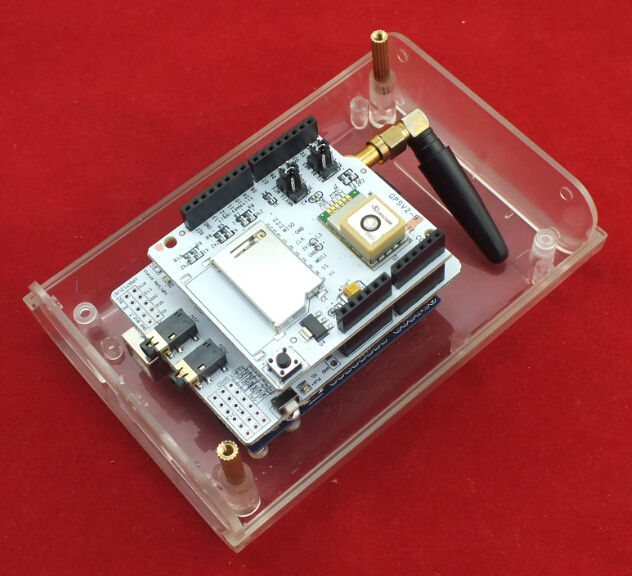
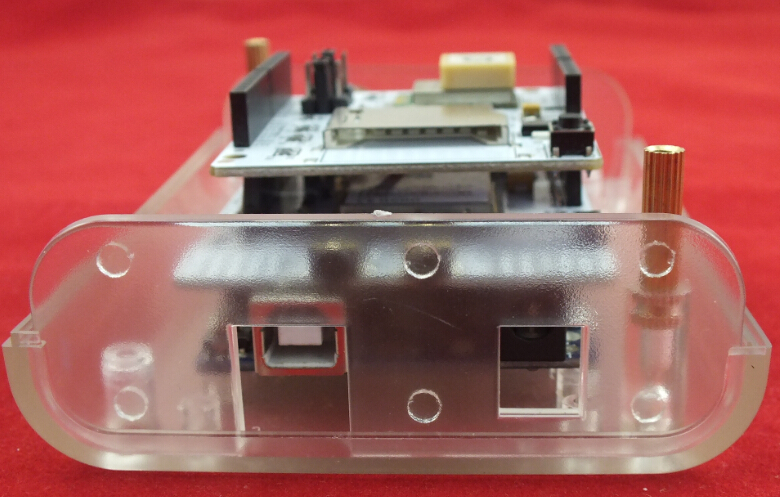
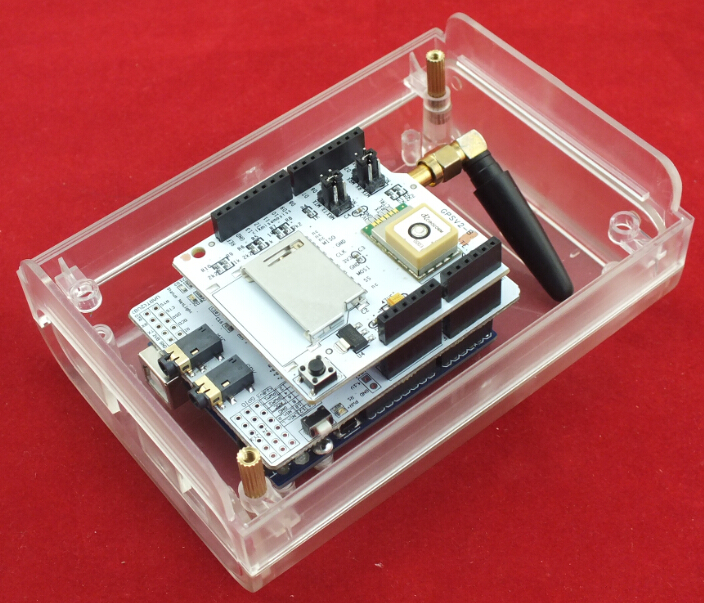
1. Fixing the Arduino UNO in the LinkSprite Clear Enclosure by screws.
2. Fixing 2 pcs Copper Pillar in the Clear Enclosure
3. Insert a SIM card in SIM GSM/GPRS Shield
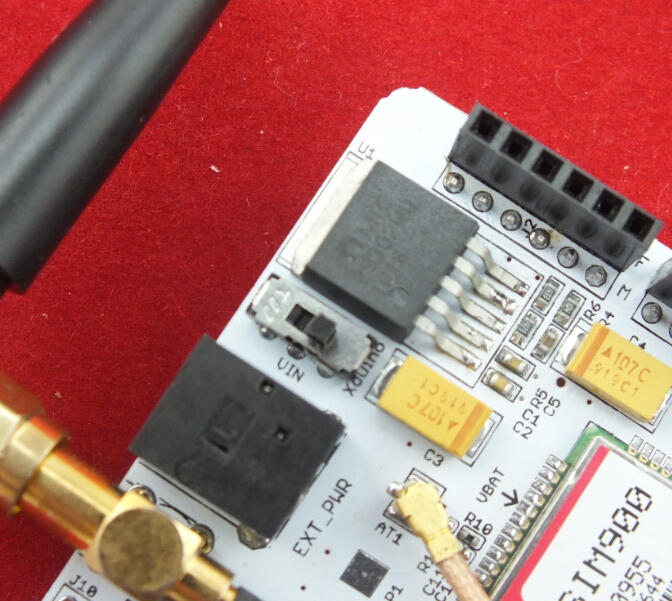
4. Push the power supply to Xduino
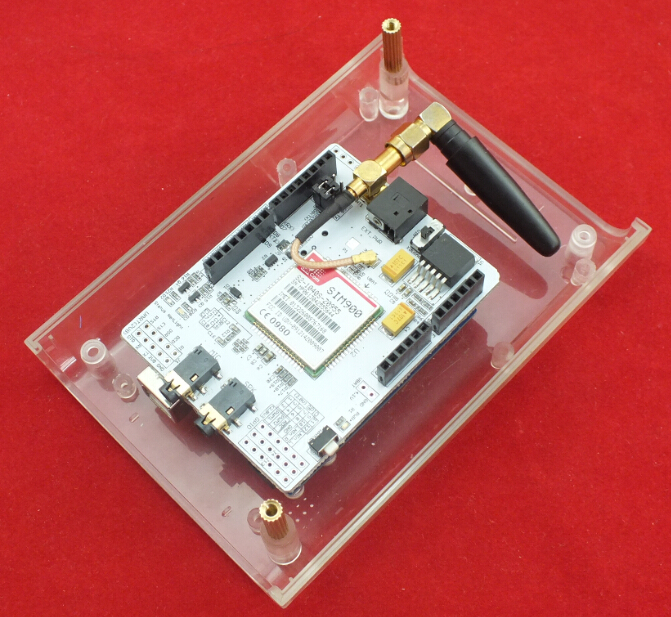
5. Plug SIM GSM/GPRS Shield into Arduino UNO
6. Plug GPS Shield into SIM GSM/GPRS Shield
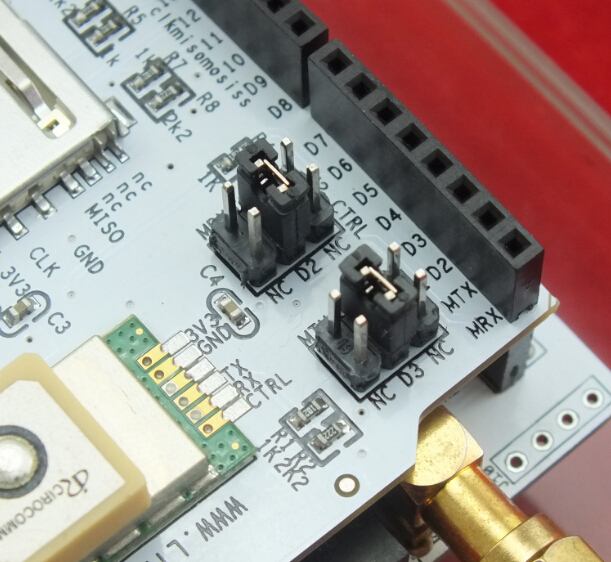
7. Choose the D2 and D3 of GPS Shield as the picture showen
8. Assembled the Clear Enclosure
Programming the Arduino
Before you can program the Arduino Uno, you must first install the Tiny GPS library for the GPS Shield. These are the steps to install the library:
1. Download the Tiny GPS library for the Arduino. 2. Extract the zip file to the folder: " Arduinobraries " 3. Now you would see the library under " Sketch --> Import Library " in the Arduino IDE. 4. You can proceed with the Arduino Uno programming.
The following is the source code for the Arduino. Copy the code below and load it on the Arduino :
- include <SoftwareSerial.h>
- include <string.h>
- include <TinyGPS.h>
SoftwareSerial Sim900Serial(7, 8); byte buffer[64]; // buffer array for data recieve over serial port int count=0; // counter for buffer array SoftwareSerial GPS(2, 3);
TinyGPS gps; unsigned long fix_age; long lat, lon; float LAT, LON; void gpsdump(TinyGPS &gps); bool feedgps(); void getGPS(); int PowerKey = 9;
void setup() {
pinMode(PowerKey,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PowerKey,HIGH); delay(3000); digitalWrite(PowerKey,LOW); Sim900Serial.begin(19200); // the SIM900 baud rate GPS.begin(9600); // GPS module baud rate Serial.begin(9600); // the Serial port of Arduino baud rate. delay(500); Sim900_Inti();
}
void loop() {
Sim900Serial.listen();
if (Sim900Serial.available()) // If date is comming from from GSM shield)
{
Serial.println("receive message");
while(Sim900Serial.available()) // reading data into char array
{
buffer[count++]=Sim900Serial.read(); // writing data into array
if(count == 64)break;
}
Serial.write(buffer,count); // if no data transmission ends, write buffer to hardware serial port
Cmd_Read_Act(); //Read the 'COMMAND' sent to SIM900 through SMS
clearBufferArray(); // call clearBufferArray function to clear the storaged data from the array
count = 0; // set counter of while loop to zero
}
if (Serial.available()) // if data is available on hardwareserial port ==> data is comming from PC or notebook
Sim900Serial.println(Serial.read()); // write it to the GPRS shield
} void clearBufferArray() // function to clear buffer array {
for (int i=0; i<count;i++)
{ buffer[i]=NULL;} // clear all index of array with command NULL
} void Sim900_Inti(void) {
Sim900Serial.println("AT+CMGF=1"); // Set GSM shield to sms mode
Serial.println("AT+CMGF=1");
delay(500);
Sim900Serial.println("AT+CNMI=2,2");
Serial.println("AT+CNMI=2,2");
delay(500);
} void Cmd_Read_Act(void) //Function reads the SMS sent to SIM900 shield. {
char buffer2[64];
for (int i=0; i<count;i++)
{ buffer2[i]=char(buffer[i]);}
if (strstr(buffer2,"linksprite")) //Comparing password entered with password stored in program
{
Serial.println("Password Authenticated.");
Serial.println("Sending reply SMS. ");
SendTextMessage();
}
} void SendTextMessage() {
Sim900Serial.print("AT+CMGF=1\r"); //Sending the SMS in text mode delay(100); Sim900Serial.println("AT+CMGS = \"**********\"");//The predefined phone number delay(100); Sim900Serial.println("Please wait while Module calculates position");//the content of the message delay(100); Sim900Serial.println((char)26);//the ASCII code of the ctrl z is 26 delay(100); Sim900Serial.println(); int counter=0; GPS.listen();
for (;;)
{
long lat, lon;
unsigned long fix_age, time, date, speed, course;
unsigned long chars;
unsigned short sentences, failed_checksum;
long Latitude, Longitude;
// retrieves /- lat/long in 100000ths of a degree
gps.get_position(&lat, &lon, &fix_age);
getGPS();
Serial.print("Latitude : ");
Serial.print(LAT/1000000,7);
Serial.print(" :: Longitude : ");
Serial.println(LON/1000000,7);
if (LAT == 0 && LON == 0)
{
continue;
}
counter++;
if (counter<30)
{
continue;
}
Sim900Serial.print("AT+CMGF=1\r"); //Sending the SMS in text mode
delay(100);
Sim900Serial.println("AT+CMGS = \"**********\"");//The predefined phone number
delay(100);
Sim900Serial.print("Latitude : ");
Sim900Serial.print(LAT/1000000,7);
Sim900Serial.print(" :: Longitude : ");
Sim900Serial.println(LON/1000000,7);//the content of the message
delay(100);
Sim900Serial.println((char)26);//the ASCII code of the ctrl z is 26
delay(100);
Sim900Serial.println();
counter=0;
break;
}
}
void getGPS() {
bool newdata = false;
unsigned long start = millis();
while (millis() - start < 1000)
{
if (feedgps ())
{
newdata = true;
}
}
if (newdata)
{
gpsdump(gps);
}
} bool feedgps() {
while (GPS.available())
{
if (gps.encode(GPS.read()))
return true;
}return 0;
} void gpsdump(TinyGPS &gps) {
gps.get_position(&lat, &lon);
LAT = lat;
LON = lon;
{
feedgps();
}
}
Also you can download the code here
Interface Function
Power select - select the power supply for GPRS shield(external power or 5v of arduino)
Power jack - connected to external 4.8~5VDC power supply
Antenna interface - connected to external antenna
Serial port select - select either software serial port or hareware serial port to be connected to GPRS Shield
Hardware Serial - D0/D1 of Arduino/Seeeduino
Software serial - D7/D8 of Arduino/Seeeduino only
Status LED - tell whether the power of SIM900 is on
Net light - tell the status about SIM900 linking to the net
UART of SIM900 - UART pins breakout of SIM900
Microphone - to answer the phone call
Speaker - to answer the phone call
GPIO,PWM and ADC of SIM900 - GPIO,PWM and ADC pins breakout of SIM900
Power key - power up and down for SIM900
Pins usage on Arduino
D0 - Unused if you select software serial port to communicate with GPRS Shield
D1 - Unused if you select software serial port to communicate with GPRS Shield
D2 - Unused
D3 - Unused
D4 - Unused
D5 - Unused
D6 - Unused
D7 - Used if you select software serial port to communicate with GPRS Shield
D8 - Used if you select software serial port to communicate with GPRS Shield
D9 - Used for software control the power up or down of the SIM900
D10 - Unused
D11 - Unused
D12 - Unused
D13 - Unused
D14(A0) - Unused
D15(A1) - Unused
D16(A2) - Unused
D17(A3) - Unused
D18(A4) - Unused
D19(A5) - Unused
Note: A4 and A5 are connected to the I2C pins on the SIM900. The SIM900 however cannot be accessed via the I2C .
A Simple Source Code Example
The demo code below is for the Arduino to send SMS message/dial a voice call/submit a http request to a website and upload datas to the pachube. It has been tested on Arduino Duemilanove but will work on any compatible variant, plesse note that this sketch uses the sorfware UART of ATmega328P. please follow the following steps for running this sketch.
- With the GPRS Shield removed, download this sketch into your Arduino.
- Disconnect the Xduino from USB port to remove power source.
- Set the Serial Port jumpers on the GPRS Shield in SWserial position, to use the Soft Serial port of Arduino.
- Connect the antenna to the GPRS Shield and insert the SIM Card.
- Mount the GPRS Shield on Arduino.
- Connect the Arduino to the computer by USB, and fire up your favorite serial terminal software on computer, choose the COM port for Arduino, set it to operate at 19200 8-N-1.
- Type command in the terminal to execute different function, threr are 4 functions in the demo:
- If you input 't', the demo will send a SMS message to another cellphone which you set(you need set the number in the code);
- If you input 'd', the program will dial a call to the other cellphone that you set(it is also need you set in the code );
- If you input 'h', it will submit a http request to a web that you want to access(it need you set the web adress in the code), it will return a string from the website if it goes correctly;
- If you input 's', it will upload the datas to the pachube(for detail you can refer to the explanation in the code). I strongly recommend you input 'h' before input 's', because uploading data to the pachube need do some setting, after execute the function of submit a http request, the setting will be set.
- If the program returns error in the terminal after you typed the command, don't worry, just try input the command again.
Note:
(1) The GPRS/GSM shield need external power supply to guarantee reliable operations.
(2) After attaching the shield to Arduino board and adding power supply, you need press the power button on the shield for about 2 seconds to turn on the shield.
<syntaxhighlight lang="c">
/*Note: this code is a demo for how to using gprs shield to send sms message, dial a voice call and
send a http request to the website, upload data to pachube.com by TCP connection, The microcontrollers Digital Pin 7 and hence allow unhindered communication with GPRS Shield using SoftSerial Library. IDE: Arduino 1.0 or later Replace the following items in the code: 1.Phone number, don't forget add the country code 2.Replace the Access Point Name 3. Replace the Pachube API Key with your personal ones assigned to your account at cosm.com */
- include <SoftwareSerial.h>
- include <String.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(7, 8);
void setup() {
mySerial.begin(19200); // the GPRS baud rate Serial.begin(19200); // the GPRS baud rate delay(500);
}
void loop() {
//after start up the program, you can using terminal to connect the serial of gprs shield,
//if you input 't' in the terminal, the program will execute SendTextMessage(), it will show how to send a sms message,
//if input 'd' in the terminal, it will execute DialVoiceCall(), etc.
if (Serial.available())
switch(Serial.read())
{
case 't':
SendTextMessage();
break;
case 'd':
DialVoiceCall();
break;
case 'h':
SubmitHttpRequest();
break;
case 's':
Send2Pachube();
break;
}
if (mySerial.available())
Serial.write(mySerial.read());
}
///SendTextMessage() ///this function is to send a sms message void SendTextMessage() {
mySerial.print("AT+CMGF=1\r"); //Because we want to send the SMS in text mode
delay(100);
mySerial.println("AT + CMGS = \"+86138xxxxx615\"");//send sms message, be careful need to add a country code before the cellphone number
delay(100);
mySerial.println("A test message!");//the content of the message
delay(100);
mySerial.println((char)26);//the ASCII code of the ctrl+z is 26
delay(100);
mySerial.println();
}
///DialVoiceCall ///this function is to dial a voice call void DialVoiceCall() {
mySerial.println("ATD + +86138xxxxx615;");//dial the number
delay(100);
mySerial.println();
}
///SubmitHttpRequest() ///this function is submit a http request ///attention:the time of delay is very important, it must be set enough void SubmitHttpRequest() {
mySerial.println("AT+CSQ");
delay(100);
ShowSerialData();// this code is to show the data from gprs shield, in order to easily see the process of how the gprs shield submit a http request, and the following is for this purpose too.
mySerial.println("AT+CGATT?");
delay(100);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+SAPBR=3,1,\"CONTYPE\",\"GPRS\"");//setting the SAPBR, the connection type is using gprs
delay(1000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+SAPBR=3,1,\"APN\",\"CMNET\"");//setting the APN, the second need you fill in your local apn server
delay(4000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+SAPBR=1,1");//setting the SAPBR, for detail you can refer to the AT command mamual
delay(2000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+HTTPINIT"); //init the HTTP request
delay(2000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+HTTPPARA=\"URL\",\"www.google.com.hk\"");// setting the httppara, the second parameter is the website you want to access
delay(1000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+HTTPACTION=0");//submit the request
delay(10000);//the delay is very important, the delay time is base on the return from the website, if the return datas are very large, the time required longer.
//while(!mySerial.available());
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+HTTPREAD");// read the data from the website you access
delay(300);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("");
delay(100);
}
///send2Pachube()/// ///this function is to send the sensor data to the pachube, you can see the new value in the pachube after execute this function/// void Send2Pachube() {
mySerial.println("AT+CGATT?");
delay(1000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CSTT=\"CMNET\"");//start task and setting the APN,
delay(1000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CIICR");//bring up wireless connection
delay(3000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CIFSR");//get local IP adress
delay(2000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CIPSPRT=0");
delay(3000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CIPSTART=\"tcp\",\"api.cosm.com\",\"8081\"");//start up the connection
delay(2000);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CIPSEND");//begin send data to remote server
delay(4000);
ShowSerialData();
String humidity = "1031";//these 4 line code are imitate the real sensor data, because the demo did't add other sensor, so using 4 string variable to replace.
String moisture = "1242";//you can replace these four variable to the real sensor data in your project
String temperature = "30";//
String barometer = "60.56";//
mySerial.print("{\"method\": \"put\",\"resource\": \"/feeds/42742/\",\"params\"");//here is the feed you apply from pachube
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.print(": {},\"headers\": {\"X-PachubeApiKey\":");//in here, you should replace your pachubeapikey
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.print(" \"_cXwr5LE8qW4a296O-cDwOUvfddFer5pGmaRigPsiO0");//pachubeapikey
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.print("jEB9OjK-W6vej56j9ItaSlIac-hgbQjxExuveD95yc8BttXc");//pachubeapikey
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.print("Z7_seZqLVjeCOmNbEXUva45t6FL8AxOcuNSsQS\"},\"body\":");
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.print(" {\"version\": \"1.0.0\",\"datastreams\": ");
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("[{\"id\": \"01\",\"current_value\": \"" + barometer + "\"},");
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("{\"id\": \"02\",\"current_value\": \"" + humidity + "\"},");
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("{\"id\": \"03\",\"current_value\": \"" + moisture + "\"},");
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("{\"id\": \"04\",\"current_value\": \"" + temperature + "\"}]},\"token\": \"lee\"}");
delay(500);
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println((char)26);//sending
delay(5000);//waitting for reply, important! the time is base on the condition of internet
mySerial.println();
ShowSerialData();
mySerial.println("AT+CIPCLOSE");//close the connection
delay(100);
ShowSerialData();
}
void ShowSerialData() {
while(mySerial.available()!=0) Serial.write(mySerial.read());
} </syntaxhighlight>
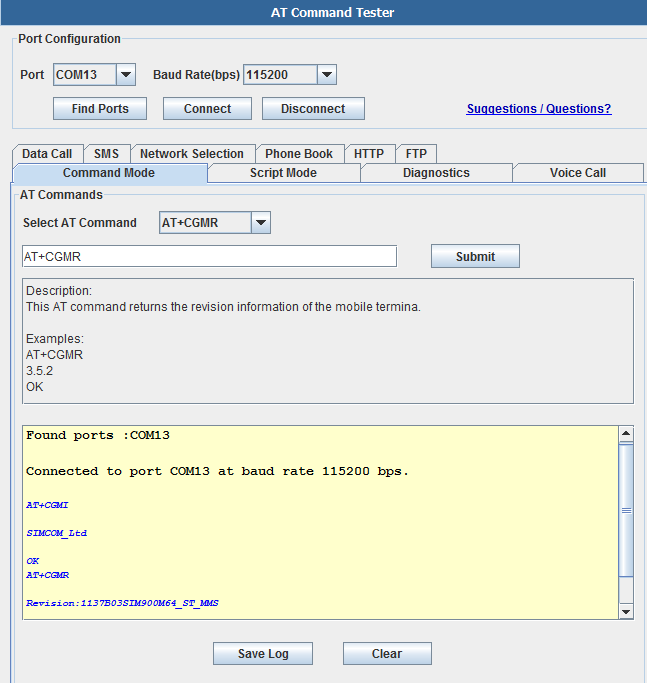
AT Command Tester Application
AT Command Tester is a free online tool test AT Commands and other modem functionalities of 2G modules (GPRS/EDGE) , 3G Modules (HSDPA/EVDO) and 4G Modules (LTE).AT Command Tester tool connects to the modem port of the device and can test various modem functions such as getting device information, gprs data call, voice call,http access, checking signal condition, network registration, SMS functions, SIM access, phonebook functions etc.
In the 'Port Configuration' section of the tool, users can search for available ports using the 'Find Ports' button. Then using the 'Connect' button, users can connect to the modem port of the device.
In the 'Command Mode' tab of AT Command Tester, single AT commands can be sent. The drop down list provides AT command description and examples. Users can modify the default command settings.
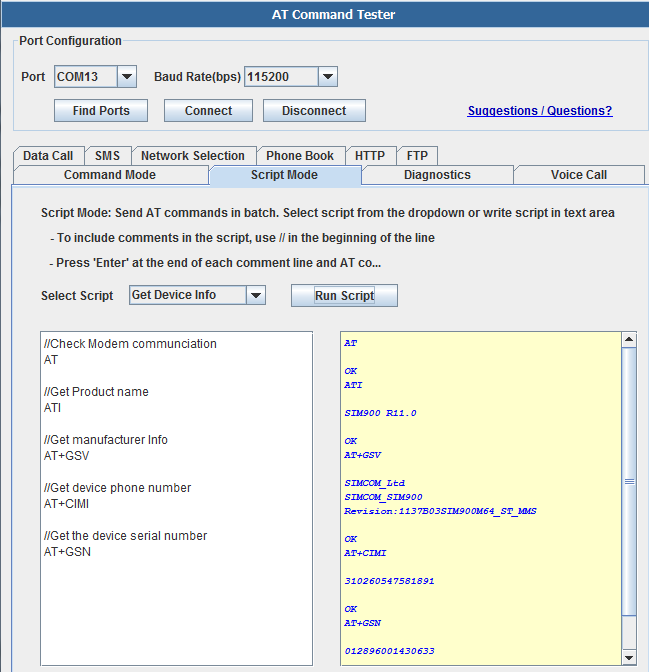
Under the 'Script Mode' tab, multiple AT commands can be sent at a time. Users can add descriptive comments and save the script on their local machine.
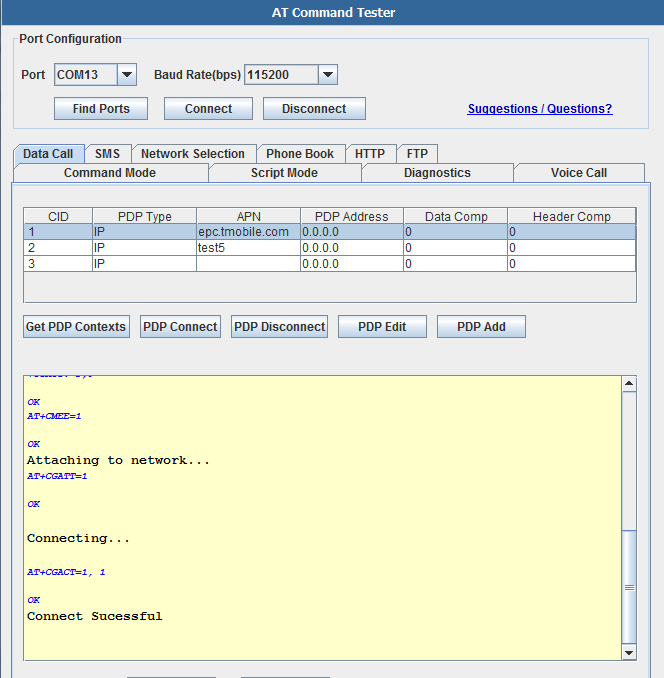
Data Call
To make a data call with the modem, you need to connect to the APN of the carrier network. The carrier APN and other required information are stored in the SIM card and are referred as PDP contexts. Typically multiple PDP contexts are stored in the SIM for different call types. With the AT Command Tester you can edit/add/delete PDP contexts in a easy to use user interface.
Typical call setup sequence,
+CGDCONT: 1,"IP","epc.tmobile.com","0.0.0.0",0,0
+CGDCONT: 2,"IP","test5","0.0.0.0",0,0
+CGDCONT: 3,"IP","","0.0.0.0",0,0
OK
Checking registration status...
+CREG: 0,1
OK
The device is registered in home network.
Checking if device is already connected...
+CGACT: 1,0
+CGACT: 2,0
+CGACT: 3,0
OK
Attaching to network...
AT+CGATT=1
OK
Connecting...
OK
Connect Sucessful
SMS
The SMS tab of the 'AT Command Tester' tool provides the interfaces to send SMS messages. You can also list/view/delete SMS messages stored on the SIM.
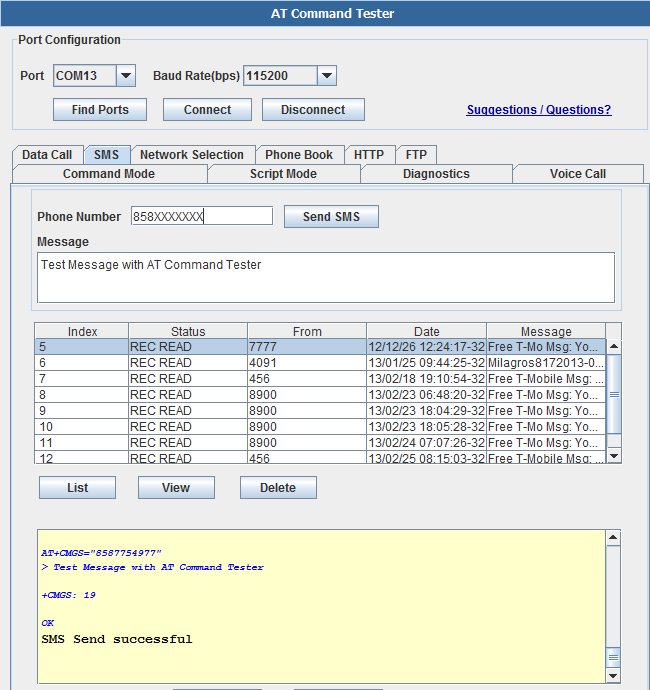
General sequence for sending SMS message,
Checking registration status...
+CREG: 0,1
OK
The device is registered in home network.
AT+CMGS="858XXXXXXX"
> Test Message with AT Command Tester�
+CMGS: 19
OK
SMS Send successful
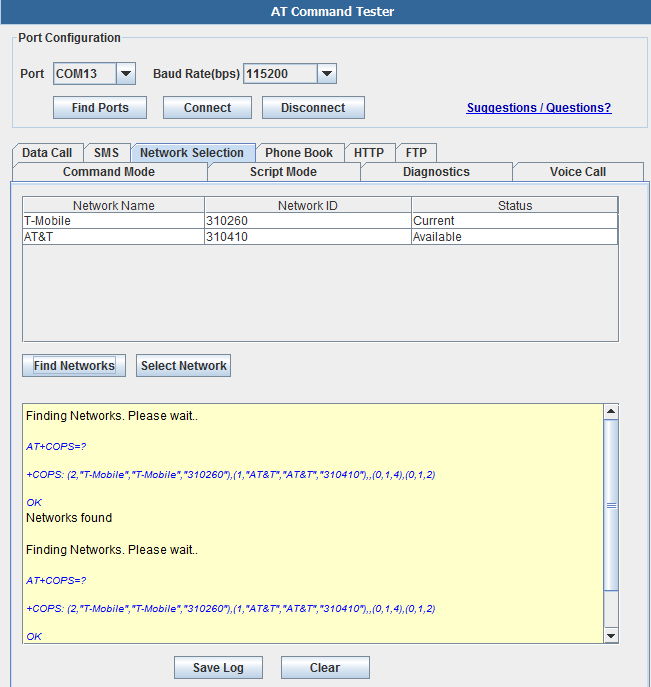
Network Selection - This tab allows the user to manually select available networks. Modems are typically set for automatic network selection. 'Find Networks' button will command the modem to scan for available networks.
AT+COPS command will initiate network scan in the modem,
Finding Networks. Please wait..
+COPS: (2,"T-Mobile","T-Mobile","310260"),(1,"AT&T","AT&T","310410"),,(0,1,4),(0,1,2)
OK
Networks found
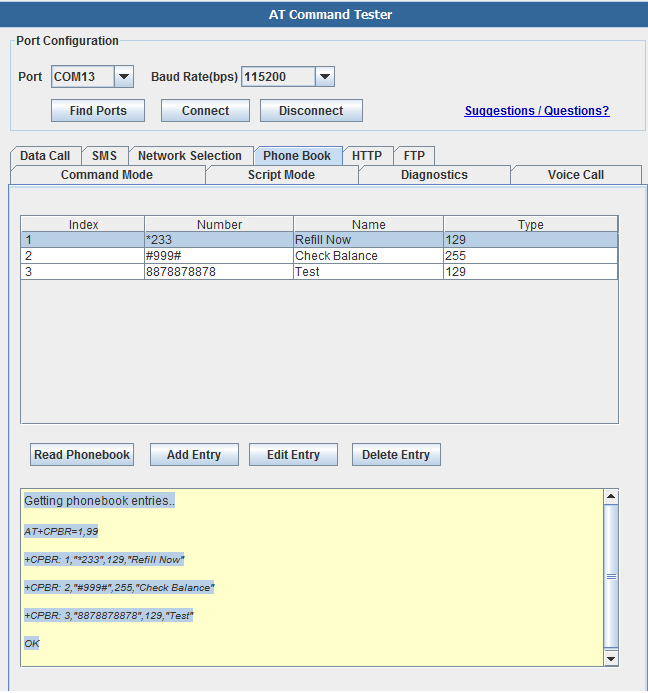
Phonebook
With the 'Phone Book' tab, you can add/delete/read phone book entries stored on the SIM,
Getting phonebook entries..
+CPBR: 1,"*233",129,"Refill Now"
+CPBR: 2,"#999#",255,"Check Balance"
+CPBR: 3,"8878878878",129,"Test"
OK
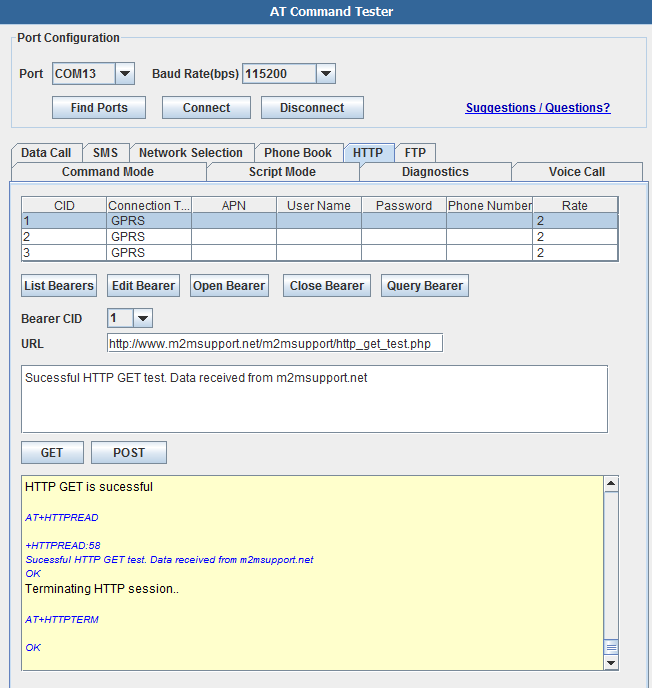
SIM900 HTTP
With the 'HTTP' tab, you can read the bearer profiles and test HTTP GET and HTTP POST,
Getting Bearer profiles..
AT+SAPBR=4,1
+SAPBR:
CONTYPE: GPRS
APN:
PHONENUM:
USER:
PWD:
RATE: 2
OK
AT+SAPBR=4,2
+SAPBR:
CONTYPE: GPRS
APN:
PHONENUM:
USER:
PWD:
RATE: 2
OK
AT+SAPBR=4,3
+SAPBR:
CONTYPE: GPRS
APN:
PHONENUM:
USER:
PWD:
RATE: 2
OK
Checking registration status...
+CREG: 0,1
OK
The device is registered in home network.
Querying bearer 1 .
AT+SAPBR=2,1
+SAPBR: 1,1,"162.184.222.162"
OK
Bearer 1 is Connected.IP address is "162.184.222.162"
Bearer 1 is Connected.
Initializing HTTP service...
OK
Error initializing HTTP service.
Setting up HTTP parameters..
AT+HTTPPARA="URL","http://www.m2msupport.net/m2msupport/http_get_test.php"
OK
AT+HTTPPARA="CID",1[[|]]
OK
AT+HTTPACTION=0
OK
HTTP GET is sucessful
+HTTPREAD:58
Sucessful HTTP GET test. Data received from m2msupport.net
OK
Terminating HTTP session..
OK
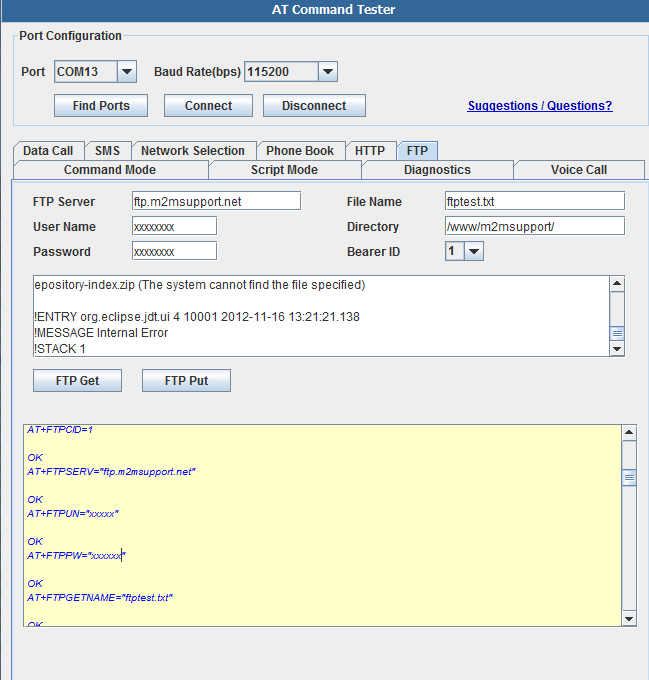
SIM900 FTP
FTP Get and Put with SIM900 module can be tested as shown below,
Checking registration status...
AT+CREG?
+CREG: 0,1
OK
The device is registered in home network.
Querying bearer 1 .
AT+SAPBR=2,1
+SAPBR: 1,1,"162.184.222.162"
OK
Bearer 1 is Connected.IP address is "162.184.222.162"
Bearer 1 is Connected.
Setting up FTP parameters..
OK
AT+FTPSERV="ftp.m2msupport.net"
OK
AT+FTPUN="xxxxxx"
OK
AT+FTPPW="xxxxxxx"
OK
AT+FTPGETNAME="ftptest.txt"
OK
AT+FTPGETPATH="/www/m2msupport/"
OK
AT+FTPGET=1
OK
+FTPGET:1,1
FTP session sucessfully started
AT+FTPGET=2,1024
+FTPGET:2,784
2-11-16 10:53:34.769 -----------------------------------------------
eclipse.buildId=M20120914-1800
java.version=1.6.0_16
java.vendor=Sun Microsystems Inc.
BootLoader constants: OS=win32, ARCH=x86, WS=win32, NL=en_US
Framework arguments: -product org.eclipse.epp.package.java.product
Command-line arguments: -os win32 -ws win32 -arch x86 -product org.eclipse.epp.package.java.product
!ENTRY org.eclipse.m2e.logback.appender 4 0 2012-11-16 12:11:54.493
!MESSAGE Unable to update index for central|http://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2: C:\Users\sgobi\.m2\repository\.cache\m2e\1.2.0\26522e0d83a422eed93329ece7565cfc\nexus-maven-repository-index.zip (The system cannot find the file specified)
!ENTRY org.eclipse.jdt.ui 4 10001 2012-11-16 13:21:21.138
!MESSAGE Internal Error
!STACK 1
OK
AT+FTPGET=2,1024
+FTPGET:2,0
OK
FTP data transfer is complete
+FTPGET:1,0
FTP session end
How to buy
Here to buy SIM900 GPRS/GSM Shield on store
FAQ
Resources
- GPRS Shield v1.4 Schematic
- AT Commands v1.00 & AT Commands v1.03 & Hardware Design - SIM900 Documentation
- Si5902BDC - Dual N-Channel 30 V (D-S) MOSFETs (used for 2.8V <> 5.0V translation for Serial Interface)
- SIM900 firmware and tool(firmware:1137B08SIM900M64_ST) for firmware upgrade
- firmware:1137B09SIM900M64_ST
- SIM900datasheeet
- Tutorial – Arduino and SIM900 GSM Modules